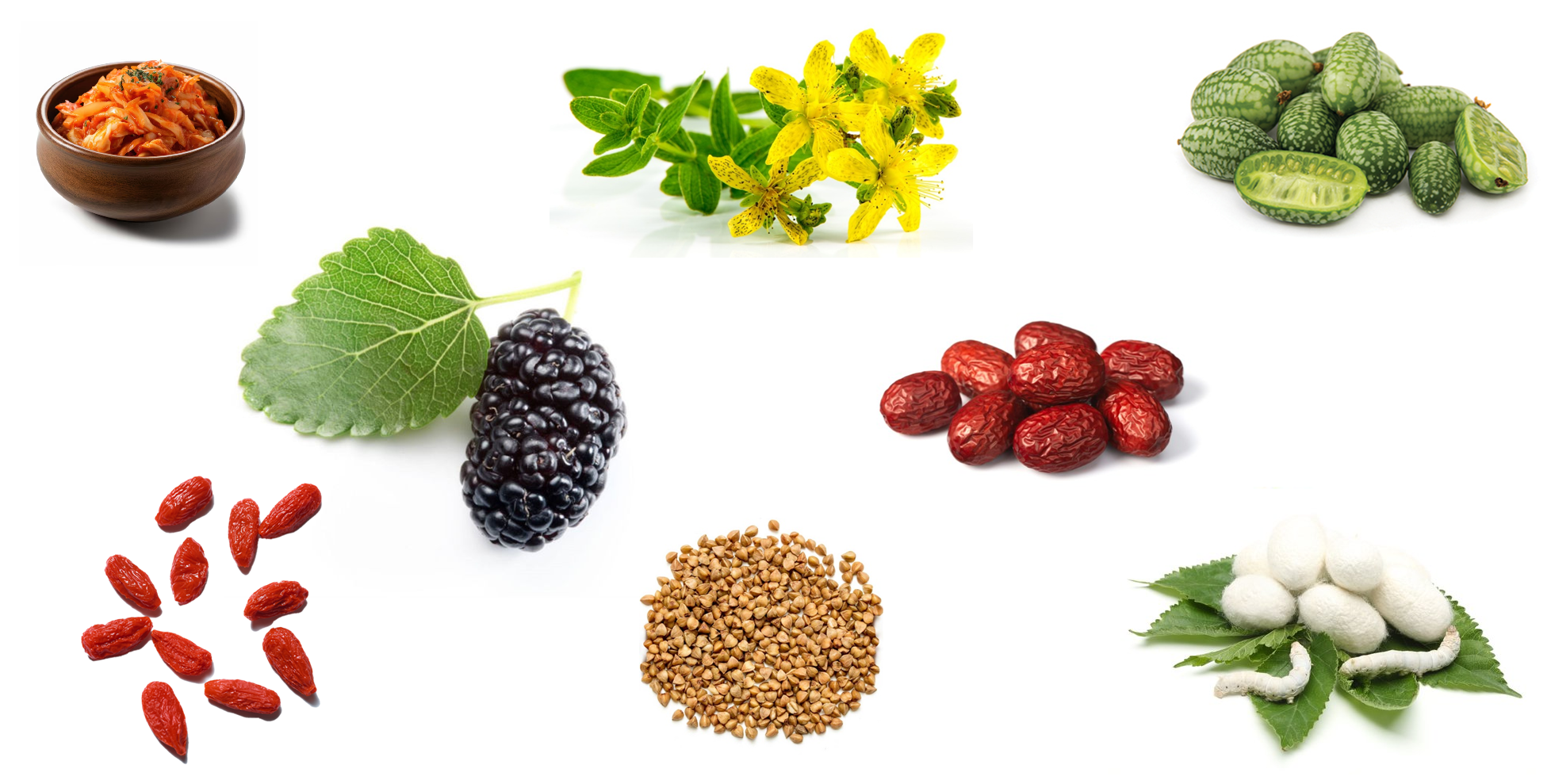
Prevalence of iminosugars in nature
Iminosugars are naturally occurring compounds found in a variety of sources, including plants, microorganisms, insects, and fermented foods. While they are less common than typical sugars, their presence in nature is often linked to defense mechanisms and specialized metabolic processes that make them biologically active and highly valuable.
In plants, iminosugars often serve protective roles. For example, the plant mulberry (Morus alba) produces 1-deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), an iminosugar known for its ability to regulate blood sugar. Other plants, such as Lobelia and Hyacinthoides, also generate iminosugars with diverse structures and applications in health and agriculture.

In the microbial world, bacteria and fungi are key producers of iminosugars, which they synthesize as secondary metabolites to gain a competitive advantage in their environments. These microbial iminosugars are of particular interest because they often exhibit potent therapeutic effects, including antibacterial and anticancer properties.
Fermented foods are another rich source of iminosugars, thanks to the metabolic activities of the microorganisms involved in fermentation. Foods like soy sauce, miso, kimchi and fermented soybeans (natto) contain iminosugars such as DNJ, which is generated by fermenting bacteria. These fermented products have been studied for their potential to improve metabolic health, particularly by inhibiting enzymes that break down carbohydrates, leading to more stable blood sugar levels. Fermented foods provide a natural, dietary source of iminosugars that may offer additional health benefits through regular consumption.
In addition to plants, microbes, and fermented foods, certain insects also produce iminosugars, where they play roles in metabolism and immune defense.
The widespread natural occurrence of iminosugars across diverse life forms suggests they have evolved as important biochemical tools, offering vast potential for human health, agricultural innovation, and biotechnological applications.
At InBio.be, we explore the natural prevalence of iminosugars across these various sources to discover and extract compounds with promising applications. By investigating their presence in plants, microbes, fermented foods, and insects, we gain deeper insights into their ecological roles and develop innovative solutions for medicine, nutrition, and sustainable agriculture.
Therapeutical applications of iminosugars
Iminosugars are a fascinating class of glycomimetics, compounds that resemble traditional sugars, where a nitrogen atom replaces the typical oxygen atom in the sugar ring. This small molecular twist gives iminosugars remarkable biological properties, making them valuable for a wide range of applications in i.e. medicine.
Iminosugars are potent inhibitors of enzymes called glycosidases, which are involved in various biological processes, including viral infections, cancer, metabolic disorders, and inflammation. For example, iminosugars have shown great promise in treating type II diabetes by slowing down the breakdown of complex sugars into glucose, thereby helping to manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, they are being explored as potential antiviral agents against diseases such as dengue, Zika, and influenza. In addition to these common applications, iminosugars have emerged as a breakthrough in treating orphan diseases—rare, often overlooked conditions with limited treatment options. For example, iminosugars have shown potential in treating Gaucher disease, Fabry disease and Niemann-Pick type C, both genetic disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies. By inhibiting specific enzymes involved in these diseases, iminosugars can help manage symptoms and improve patients’ life comfort.
Discovery of new iminosugars
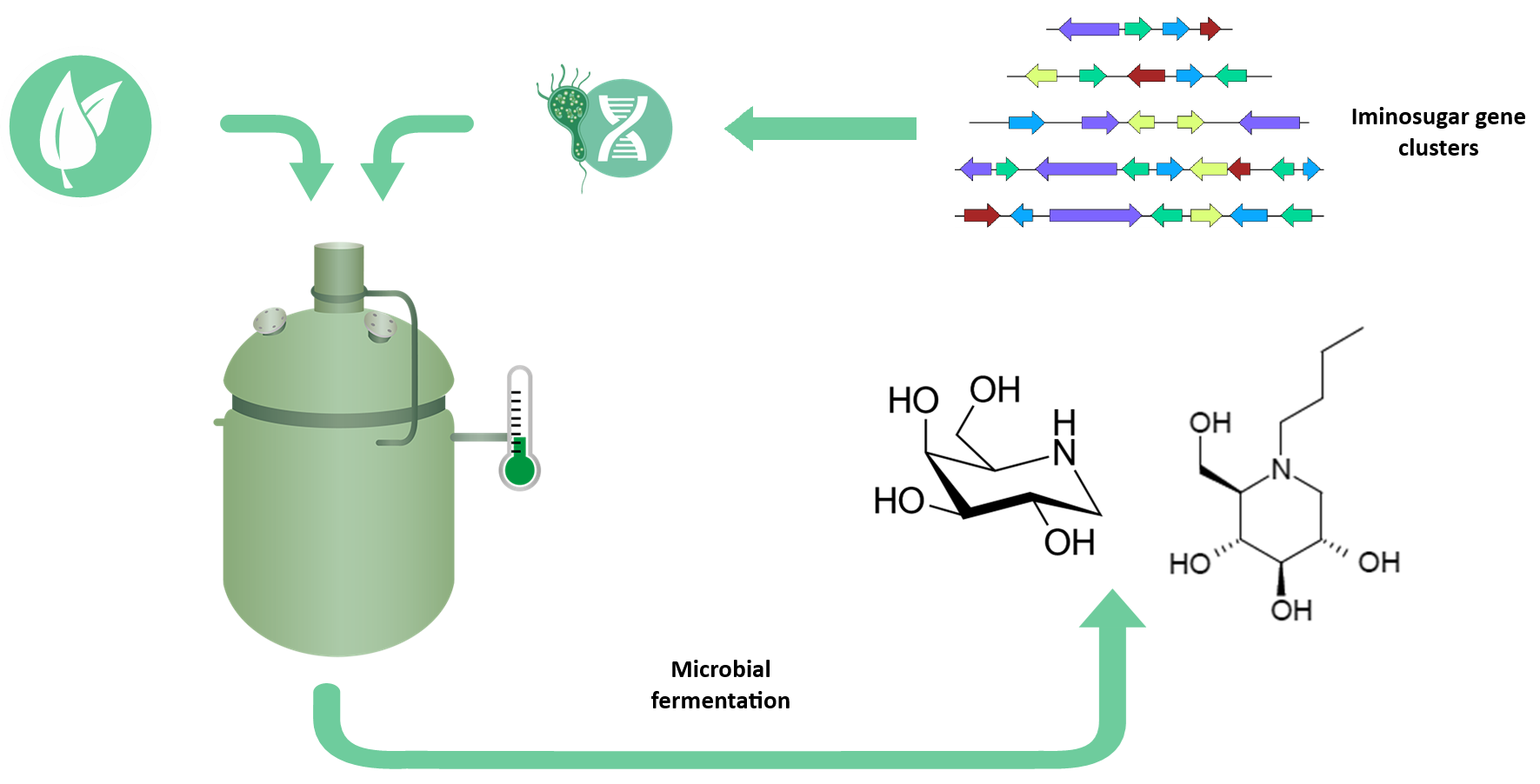
The discovery of new iminosugars is an active and rapidly evolving field of research. While some iminosugars occur naturally in microorganisms and plants, many remain undiscovered, hiding in the metabolic pathways of lesser-known species. At InBio.be, we are pioneering the search for novel, microbial iminosugars by exploring natural and engineered microbial systems.
We employ advanced techniques such as genome mining and metabolomics to identify biosynthetic gene clusters responsible for iminosugar production. These tools allow us to dig deep into the genomes of bacteria and fungi, uncovering new pathways that lead to the synthesis of iminosugars with unique structures and activities. Additionally, our research extends beyond known microorganisms; we investigate uncultured microbial communities in their natural environments through metagenomics, providing access to new sources of bioactive molecules.
Our goal is not only to discover new iminosugars but also to understand their mechanisms of action. These fundamental insights allow us to better predict and implement iminosugar gene clusters for enhanced bioprocess development.
Biomanufacturing of iminosugars
While the discovery of new iminosugars is exciting, the biomanufacturing of these compounds is equally crucial for their practical application. At InBio.be, we are developing sustainable, microbial-based production systems to produce iminosugars at scale, transforming microorganisms into efficient cell factories.
Through synthetic biology and metabolic engineering, we optimize microbial strains to enhance the production of iminosugars. By modifying the biosynthetic pathways within microorganisms, we are able to increase yield, improve purity, and reduce the environmental footprint of iminosugar production compared to traditional chemical synthesis or extraction.
Moreover, we focus on developing scalable bioprocesses for the fermentation and purification of iminosugars, ensuring that these valuable compounds can be produced in sufficient quantities for industrial use. Our biomanufacturing approaches hold promise for a wide range of industries, from pharmaceuticals to sustainable agriculture, where iminosugars can be used in innovative and impactful ways.
At InBio.be, we are committed to advancing both the discovery and production of iminosugars, contributing to their broader application and harnessing their potential for a healthier, more sustainable future.